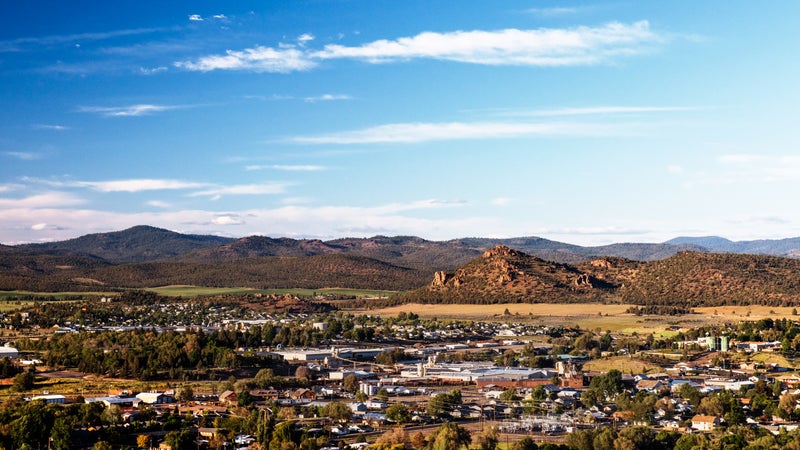
How Big Data Saved the Mountain Town
How does a town go from logging and livestock to bits and bytes? Tiny Prineville, Oregon, is finding out as huge data centers from Apple and Facebook transform the timber town into a recreational hub of mountain bikers and craft brewers.
New perk: Easily find new routes and hidden gems, upcoming running events, and more near you. Your weekly Local Running Newsletter has everything you need to lace up! .
On Main Street in Prineville, Oregon, across from a saddlery that has seen better days, sits a 75-year-old bar called the Horseshoe Saloon. The clientele here is a mix of ranchers, out-of-work lumberjacks, libertarian hippies, and one-armed electricians. People like to dress up at the Horseshoe. At a recent white-trash-themed costume party, a bartender wore a T-shirt that read HE BROKE MY <3 BUT WE STILL BE COUSINS. A sign over the bar advertises a 30-day ban for those caught fighting. It’s not decorative. One Prineville resident advised me to avoid the Horseshoe unless I want to witness or participate in a fight.��Another said, “You might be able to have a beer and get out of there in one piece.” He had served in both Operation Desert Storm and the 2003 Iraq invasion.

for your iPhone to listen to more longform titles.
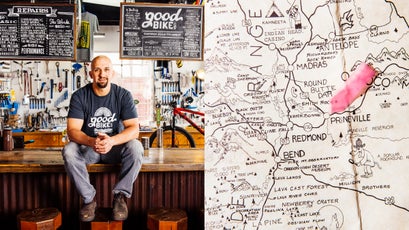
On a Sunday morning last October, I found myself seated at a table in the Horseshoe alongside three recent Prineville transplants: a goateed bike-shop owner named James Good; his wife, Natalie, a family doctor who’d been recruited by the town; and Greg Stump, or “Stumpy,” the 57-year-old ski filmmaker who directed the 1988 cult classic Blizzard of Aahhh’s. The Goods, who are in their thirties, live in a spacious cedar house in the foothills of the rugged Ochoco Mountains. In 2014, they moved from Ogden, Utah, where James worked for the climbing company Petzl. The first time they came to Prineville, population 9,928, they drove past the gas station advertising $1.50 biscuits and gravy and the Prepper Up ammo store with the Confederate flag in the window. Natalie, who grew up in Oklahoma, was set on moving to a rural town like Prineville. But, she told me, “It was hard to convince James.” Ogden had sushi, Thai, and a ski resort; Prineville had a Tastee Treet and a steakhouse featuring video gambling machines. But the city was dogged in its recruitment, the Goods left Utah, and James opened , which offers sales, tours, and craft beer. Now James was warming to Prineville, on account of its unpopulated wilderness and warm community. The town’s largest civic gathering is a rodeo with a cattle drive down Main Street. “At first I was like, I don’t think I can do this,” he told me. “Now I’m like, How did we figure this out?”
From here one can catch trout on the blue-ribbon Crooked River, climb at Smith Rock, mountain-bike or backcountry-ski in the Ochoco National Forest, or cycle buttery roads through high-desert juniper and sagebrush
Bob Seger sang on the jukebox, and I ordered a dish called the Garbage Scramble, which arrived pretty much as advertised. We were loading up on calories in order to ride Lookout Mountain, a 6,900-foot peak with a resident wild horse population. The Goods seemed charmed by the Horseshoe, as it was one of their first trips here.
Stumpy, on the other hand, had become something of a regular since moving to Prineville in 2015. The filmmaker, who derives his nickname in part from his stature, has long blond hair that’s often spouting over the top of a silver bandana. He relocated here after a decade in the Tetons, and he too had to overcome early skepticism. When he visited the property that he was considering for renovation—an old doll factory that had been in his girlfriend’s family—he encountered feral cats and a condemned notice. But Stumpy sensed that Prineville was on the verge of a renaissance.
Despite its boots-and-hat veneer, Prineville, Oregon, is a primary driver of America’s next great boom industry. In 2010, Facebook broke ground on a billion-dollar data center here in Crook County, its first; . The two tech giants now operate in close proximity to one another, on a bluff just west of town. Stumpy and others have been drawn by this economic influx—but also by Prineville’s incredible outdoor access. From here one can, within a 30-minute drive, catch trout on the blue-ribbon Crooked River, climb at Smith Rock, mountain-bike or backcountry-ski in the , or cycle buttery roads through high-desert juniper and sagebrush. “I fixed up two houses in Maui,” Stumpy said. “I’ve seen Telluride. I could have bought a shack there in ’83 for ten grand.” He believed that Prineville was about to pop. James Good agreed. “Everyone’s afraid of it becoming the next Bend,” he said, referencing the nearby adventure-sports hub.��
Behind us, a server offered an impassioned discourse on why Bailey’s should be classified as creamer rather than alcohol. Then Stumpy abruptly rose and started crashing around the bar, reenacting the antics of a drunken rodeo cowboy he’d recently seen here. The Goods and I left, heading up to an empty trailhead surrounded by towering conifers. James zipped off and I followed, ascending soft duff singletrack through towering ponderosas; the occasional larch peeked out gold. We saw no one else.
It started to snow. First a little, then a lot, until the flakes hardened and blew uphill in a fierce wind, stinging our faces. “We should get off this,” James said. Soon we were in a low-grade whiteout, trying to make it through the no-fall zone on the far ridge before the snow swallowed up our trail. Thirty-six miles away, people were ordering lattes in Bend. That sounded dull.��
Prineville should be a ghost town. Ten years ago, the place was poised to become one more rural victim of technology, globalization, and regulation. For a snapshot of what might have been, one need only drive past the Horseshoe and up a small hill. Here sits an abandoned mill-products factory with a caved-in roof, across the street from a cemetery. It could have been the cover of a Bruce Springsteen album. Prineville, named for an early settler, was built on timber, and the place boomed in the mid-20th century, thanks to its proximity to the railroad and abundance of pine trees. Timber fallers came to work at five saw mills; ranchers ran cattle; the area became a hub for rock hounds collecting agates in the volcanic high country. Les Schwab, the son of a logger, opened a tire store here in 1952 and gave away free beef to customers in the slow winter months.
Rural towns don’t often die overnight. What happens is more like a slow bleed followed by a knockout blow. As the West’s natural-resource-based economy faltered, Bend invested heavily in tourism and grew from about 17,000 residents in 1980 to 87,000 today. Prineville opted for stasis, continuing to log old-growth ponderosa. The timber industry eventually faltered when the Forest Service decreased sales due to public concerns about overharvesting statewide. Litigation over endangered species habitat further handicapped the business. Hang around town long enough and you’re likely to see a bumper sticker reading I LOVE SPOTTED OWL—FRIED.

The first of Prineville’s five mills to close did so in the early eighties, the last two in 2001. Then came the financial crash. The secondary timber-products industry crumbled, and in 2008 Les Schwab moved its headquarters to Bend. Overnight, Prineville suffered 18, 19, then 20 percent unemployment, the highest in the state. A thousand people—a tenth of the town—moved away. Local kids sold firewood out of the backs of trucks; some joined the thriving meth trade.��
In 2008, town leaders, including mayor Betty Roppe, a spirited Republican great-grandmother who is now 77, began receiving e-mails from a company using the code name Vitesse. (This is a common practice in the hypersecretive tech community, both as a matter of culture and to prevent competitors from moving in on good sites.) Vitesse said it was interested in opening a data center, one of the sprawling buildings used by tech giants to house their racks of servers. Virtual life—social media accounts, iCloud storage, every ski video you’ve ever saved—requires physical space to house all those bytes. The space must be cool, dry, cheap, and within range of transmission stations, power lines, and fiber-optic networks, which frequently run along railroad lines.��

After relying for years on second-party facilities, giants like Amazon and Microsoft began seeking their own territory in the mid-2000s. , powered by dams on the Columbia River. Virginia and North Carolina became early hubs, in part because of abundant coal- and gas-fired power plants and fiber-optic networks. By 2010, data centers were using nearly 2 percent of the nation’s electricity. Facebook, meanwhile, also scouted the Northwest, with its cheap energy (powered primarily by coal from the intermountain West and hydro from the Columbia and Snake River dams) and cool, dry climate (particularly in its eastern region). Data centers require a lot of energy and water for the cooling systems that keep their servers from overheating. A large data center can use enough energy to power a small town.��
When Roppe and her colleagues at city hall first got the e-mail from “Vitesse”—Facebook—they responded like a trout taking a fly. But Facebook was also talking to other towns. Prineville needed assurances about the number of workers that would be hired from Crook County; Facebook wanted a tax break. Prineville informed Facebook that the company would need to install a city-approved sewer line and access roads; Facebook wanted to make sure that there were no endangered species that might block construction. During negotiations, one city official recalled, Prineville’s unemployment rate reached 22.8 percent. The town struck a deal, offering Facebook a 15-year abatement on property-improvement taxes in exchange for an annual $110,000 payment and millions of dollars in other charges. Facebook agreed to make good-faith efforts to hire locally—and to pay 150 percent of the median Crook County salary. When Mark Zuckerberg showed up for the groundbreaking, Facebook representatives politely suggested that town leaders refrain from placing a cowboy hat on his head.��
In 2012, . It, too, used a code name—Pillar—and received a similar tax break. It, too, opened a data center on the bluff above town. Construction workers poured in from Portland and Arizona. Unemployment fell to 7 percent, rent doubled, and the town’s hotels filled.��
When I called the Rustlers Inn to make a reservation, the woman who picked up the phone asked if I was a construction worker. I said no. She paused and said, “You’re not one of the homeless, are you?” I said I wasn’t—that I was a writer coming to report on the town’s resurgence. She repeated her suspicion that I was a vagrant and hung up.
The road to Prineville from Bend passes cattle pastures and juniper stands. Soon a driver reaches the edge of a bluff. To the south, the Crooked River curls into a canyon, to the northeast loom the Ochoco Mountains, and down below sits the Mayberry-ish grid of Prineville. Apple and Facebook are perched on the edge, as though overlooking their domain.
The two data centers adhere almost comically to their company’s reputations. Facebook’s sleek buildings are decorated with Black Lives Matter posters and a company mantra, “Ship Love.” Apple’s center is sterile—white and gray, with no visible aphorisms. Visitors to Facebook see a fleet of bicycles from Good Bike Co. parked out front; visitors to Apple are greeted by a security gate that seems worthy of the FBI. Facebook has a game room with a pool table; early on, Apple employees wouldn’t tell locals where they worked. “We don’t play by those rules,” the Facebook data center’s then-director of operations, Ken Patchett, told me with a wink when I visited last October. “We’re a social company.”
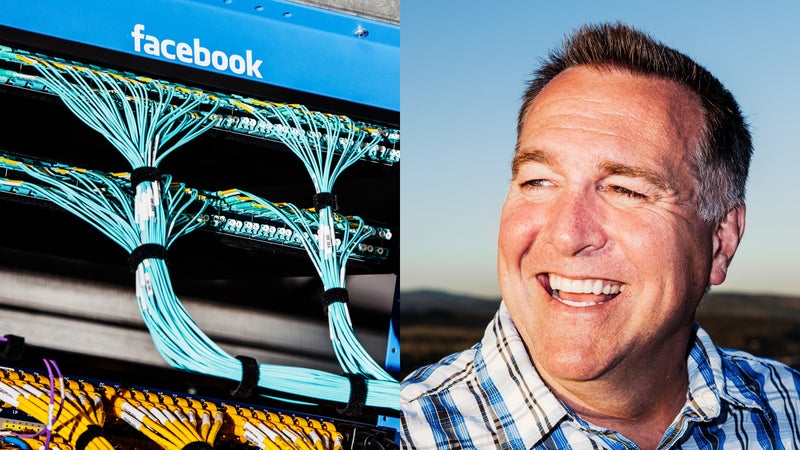
At Facebook, a local chef served steaks in a lively cafeteria full of workers. Some wore hoodies and sneakers, others construction vests. “The Internet is not a fake thing,” Patchett told me, his blue eyes twinkling. He’s a large, 48-year-old man with a crew cut who came to tech after working in the paper-pulp industry in Seattle. “It’s a very, very real thing made with hammers and concrete. And nails. And blood and sweat and tears and people.”
Patchett was very into the blue-collar nature of the enterprise here, and it’s true that data centers are at their core industrial affairs—essentially, byte warehouses. When I visited, Facebook’s Prineville center employed 186 people, 75 percent from Crook County, Patchett said. Patchett, who lives in Bend and has the gusto of an entrepreneur, pointed out some black-and-white photos of Prineville’s settlers. “The pioneers who built this town are no different from us!”
With him were a publicity representative and a local employee named Ristine Williams. Williams distributes some $100,000 in Facebook community grants per year, funding, for example, a new sound system for the high school stadium. Before signing on with Facebook, she worked three part-time gigs to support her two children. “Everyone was fighting for the same jobs,” she said. Recalling the hard days caused her to tear up momentarily.��
We walked down a hallway toward a distant humming. We passed some more photos of cattlemen, then went through a door to find a series of large photos: of cave paintings, Martin Luther’s theses, a sheet of newsprint, a laptop, a smartphone. Patchett paused for effect and asked, “Do you know what Facebook is? Like what you’re in? What it really means?”

His voice sped up and rose a decibel. He started at the representation of early pictographs, saying, “Since the beginning of time, mankind has always had the need to share,” then moved on to a photo of Egyptian hieroglyphs and the dawn of science and reason, stuck in an odd aside about aliens, then skipped a few thousand years to the . (“You can’t e-mail that! You had to go to it!”) In a flash we landed at the American Revolution, the typewriter, the telegraph, and the radio. “Most people don’t get a chance to be on the radio, to share their thoughts, their hopes, their dreams. Does that mean they’re not important? Does that mean they don’t matter? I’ll leave that hanging for a minute.” Except Patchett didn’t leave it hanging for even a millisecond, because now it was on to the computer, TV ads, and Nerf guns before finally, mercifully, we reached the apotheosis of human communication: the Facebook-enabled smartphone. And here we came back to Patchett’s original question, the big one that existentialists have been grappling with for 13 years: What is Facebook?
“Facebook,” Patchett said, “is always you. You are the person who makes Facebook what it is. Because it’s you! Always.” He did, however, concede that it can be “leveraged as a branding engine.”
The thrumming sound got louder as we walked into a dark, cavernous room. Rows and rows of flashing blue servers marched into the distance, holding billions of virtual lives. “Isn’t that pretty?” Patchett asked. “Sexy, man.”
The air was pleasant, thanks to great fans sucking Prineville’s dry, temperate air from the outside through watered membranes. The effect is something like a massive swamp cooler. This is where Facebook uses the majority of its water—18 million gallons per year. (Apple’s Prineville center, for its part, used 29 million gallons last year.) Forty percent of that evaporates in cooling; the rest is recirculated or discharged. In winter and on most nights, no cooling is required.��
We emerged into a hallway adorned with a mural of cowboys thumbing iPhones. A photo showed a sepia-toned cowboy on a bucking bronco. This was Patchett’s favorite. “This is us,” he said, gesturing to the cowboy. “And this”—the horse—“is the Internet. We’re just trying to ride it and do the right thing.”
I walked out to my rental car feeling like it might be wise to delete my Facebook account. The Ochocos loomed beyond. But it was election season. As soon as I sat down, I looked away from the mountains, buried my head in my iPhone, opened Facebook, and checked the latest news.��
Prineville is the kind of place that holds tightly to its extractive past, where people have more guns than they need and fewer than they want. For places like this, there aren’t many options: you can pray for a return to past glories or you can move along.��
For many struggling natural-resource towns, data centers have become a Hail Mary. A company that provides security for the Bitcoin network recently moved into an abandoned sawmill in Bonner, Montana, on the Blackfoot River, and in a former coal-fired power plant in Alabama. Wyoming, a foundering coal state, .��
As far as big businesses go, towns can do much worse than attract a data center, according to Jonathan Koomey, a Stanford lecturer who has tracked the industry for the past two decades. “It doesn’t pollute, and there aren’t huge noise issues,” says Koomey.
Prineville is where the Oregon of the Bundy occupation meets the Oregon of “Portlandia.”
Lately, tech companies have also been spurring development in renewable energy. Apple, Facebook, and other big outfits got some dismal reviews in a Greenpeace report five years ago, but many now negotiate access to renewables as a condition for moving into an area. Apple did just that when coming to Prineville, securing local wind energy at a long-term fixed rate and financing its own micro-hydro sites on an irrigation canal off the Crooked River. I toured Apple’s facilities in November, led by site manager Scott Moore, a 47-year-old Texas cowboy and rodeo fan. None of what he said during that trip will be made public here; in keeping with its Fight Club reputation, Apple wouldn’t allow me to quote anything said during our tour. But the sites were impressive, a series of small turbines set off the main channel of the Crooked. Together they provide about 5 percent of the data center’s electricity. The rest comes from wind and a forthcoming solar farm the company paid for.��
Facebook still runs its Prineville facility off Pacific Power’s coal-dominated mix, using enough energy to power 26,000 homes. But it has committed to running all its future data centers off renewables and has actively pushed utilities away from fossil fuels, for example, in Nebraska.
However, there’s always a catch with big business. Sawmills lead to clear-cuts, coal mines scar the land, and meatpacking plants stink. Data centers have few major negatives, but they lack that critical positive: they create relatively few jobs. Traveling around Prineville, I frequently heard complaints along these lines. A saddlery owner named Hank, with a waxed mustache that appeared capable of spearing marshmallows, said, “Hell, we’re glad with what we got. But the mills employed 1,500 people. Not 30.”
This was a constant rumor: that Facebook employed just 30 people, and that it would leave in 15 years, when the tax break was up. It drove Ken Patchett crazy. “Does it look like 30 jobs to you?” he demanded during my tour. As of this writing, Facebook employs more than 200 people in Prineville, not counting temporary construction workers; Apple, 140.��
Still, Roppe and her colleagues aren’t naive. The possibility of the companies leaving seems remote, given their billion-dollar investment and the pace at which Americans are consuming data. But the way Prineville officials see it, they’ve got a decade and a half to reimagine the town. And if Apple and Facebook leave, local leaders like to say, they’ll have the world’s largest hay sheds up on the hill.��
In November, Mayor Roppe took me on a tour of a new civic project just beneath the bluff: a . It consisted of eight descending ponds, 40,000 native plants, a five-mile greenway, and a newly carved-out river channel to allow the Crooked to meander in its natural floodplain. (In the early 1960s, the Army Corps of Engineers had straightened the channel for flood control.) The entire project cost almost $9 million, half of which came from environmental grants and much of the other half from the annual fees collected from Apple and Facebook. “It’s going to be fantastic,” Roppe said while steering a white pickup through the area. It still looked stark, a series of ponds surrounded by dirt, with guys in hard hats marching around. But the river had been rechanneled to create habitat for juvenile fish, including steelhead; bat boxes were interspersed between transplanted native willows, and the greenway wove throughout the ponds.
Roppe occasionally paused to honk at geese and proudly told me about her nine great-grandchildren, all of whom live in Oregon. “We need living-wage jobs,” she said. “Without them the youth don’t stay.” Roppe saw the tech surge as an opportunity to diversify, including through tourism. She thought the wetland project might bring birdwatchers. She wanted more businesses like Good Bike Co. in town.
Prineville certainly has the adventure-sports offerings to match almost any town in the West. I asked Roppe about the concern that Prineville could eventually become like Bend. “We don’t want to be Bend,” she replied sharply. I asked how big she thought it would get, and she said 20,000, citing the estimate of one local economist. But thirty years ago Bend’s population was less than 20,000.
People like to say that Bend is 30 miles from Prineville but Prineville is 90 miles from Bend, meaning that the yuppies mostly stay away. That seems likely to change in coming years, a terrifying prospect to many locals. Shortly after working me over in a game of eight ball, a pool shark at the Horseshoe told me that the techies were destroying the town by jacking up rent. He was living in a friend’s garage. Other concerns were—how to put it?—more philosophical. One day at the bar, I met a long-haired guy who identified himself as an amateur expert in cryptogamic crust. “We are not more important than this land,” he told me. “And turning those yuppie sons of bitches loose on it is the end of it.” Then he veered off into a rant about Muslims.
Two doors down from my hotel was Prepper Up, the survival store. The decor included a tribute to LaVoy Finicum, who was killed early last year by federal agents after occupying the , 160 miles east of here. I asked a large man behind the desk what he thought of Facebook. He was a fan—both his daughter and grandson worked there. A lean twentysomething with a pistol strapped to his thigh named Sean was astounded: “That Facebook? Cool! Is that where Mark Zuckerberg works?”
People like to say that Bend is 30 miles from Prineville but Prineville is 90 miles from Bend, meaning that the yuppies mostly stay away. That seems likely to change in coming years, a terrifying prospect to many locals.
The owner of Prepper Up, a slim man from Georgia with gray hair named Ray, conceded that the companies were good for the local service economy but expressed concern over the flooded housing market. He was also worried that Apple and Facebook might bring in more Democrats and “California laws”—that is, gun control. If the town changed too much, he said, he might head east, to Idaho. Sean nodded gravely.��
The collision here is cultural. Prineville is where the Oregon of the Bundy occupation meets the Oregon of Portlandia. One night I went to meet Stumpy for dinner at the , a microbrewery that opened just after Facebook arrived. He wore his customary bandana and told stories about hanging out with Willie Nelson in Maui. It was open-mic night, and a cowboy band full of teenagers in boots and hats tuned up their instruments. Then a skinny punk kid with a guitar covered in stickers introduced a song. “This one’s called ‘Facebook,’ ” he said. “You created a bunch of selfies,” he howled. “Electronic lobotomies! Now hear this: WE’VE CREATED A BUNCH OF ZOMBIES!”
It was a long winter in eastern Oregon, the kind that normally shuts a place like Prineville down. But this season was different. At Facebook, hundreds of workers pushed ahead on a third server hall; at Apple, the construction of a fourth building hummed along. In January, a new brewery opened. It had an open industrial floor plan and could have fit in well in Seattle. The news wasn’t all good, though. That month, a manufacturer calling itself Project Falcon had hit pause on a prospective deal to open a factory with hundreds of blue-collar jobs, out of concern that the city might not be able to provide enough electricity. The city claims it has since worked this out with the utility, but the perception was that Apple and Facebook were hogging the grid.
Around that time, commuters noticed something new near the wetland project: eagles. Lots of eagles. The wetland had provided a home for waterfowl, and the predators seemed to have followed them. Then, in April, the willows and wood rose started to bud.
I reached out again to Scott Moore, the cowboy running the Apple data center, and eventually convinced the company to let him speak to me on the record. He told me that he had been living half an hour away, outside Redmond, but was looking at property in Prineville, partly because he wanted a place to raise his horse, five heifers, 20 sheep, and assorted chickens and goats. “I want more property and to live in the country, and I want to live in the community I work in,” he said. Ken Patchett, on the other hand, had moved on, leaving Facebook for a “stealth startup,” splitting his time between Bend and California.��
Around the same time, the U.S. Census Bureau released its latest data. Last year, , making it the eighth-fastest-growing county in the U.S. The data rush, it seemed, was on, and when I heard the news I felt a twinge, an old-fashioned tug toward the shifting mirage that is the American frontier. A part of me wanted to live in Prineville, too. A part of me already did.
Contributing editor Abe Streep () wrote about climber Dave Morton in April 2016.